钩子函数在Linux系统中的应用与实现
钩子函数
钩子函数(Hook Function)是一种编程技巧,它允许开发者在不修改原有代码的情况下,向某个事件或过程添加自己的逻辑,在Linux系统中,钩子函数被广泛应用于系统调用、进程管理、文件系统操作等多个方面,为开发者提供了极大的便利。

钩子函数在Linux系统调用的应用
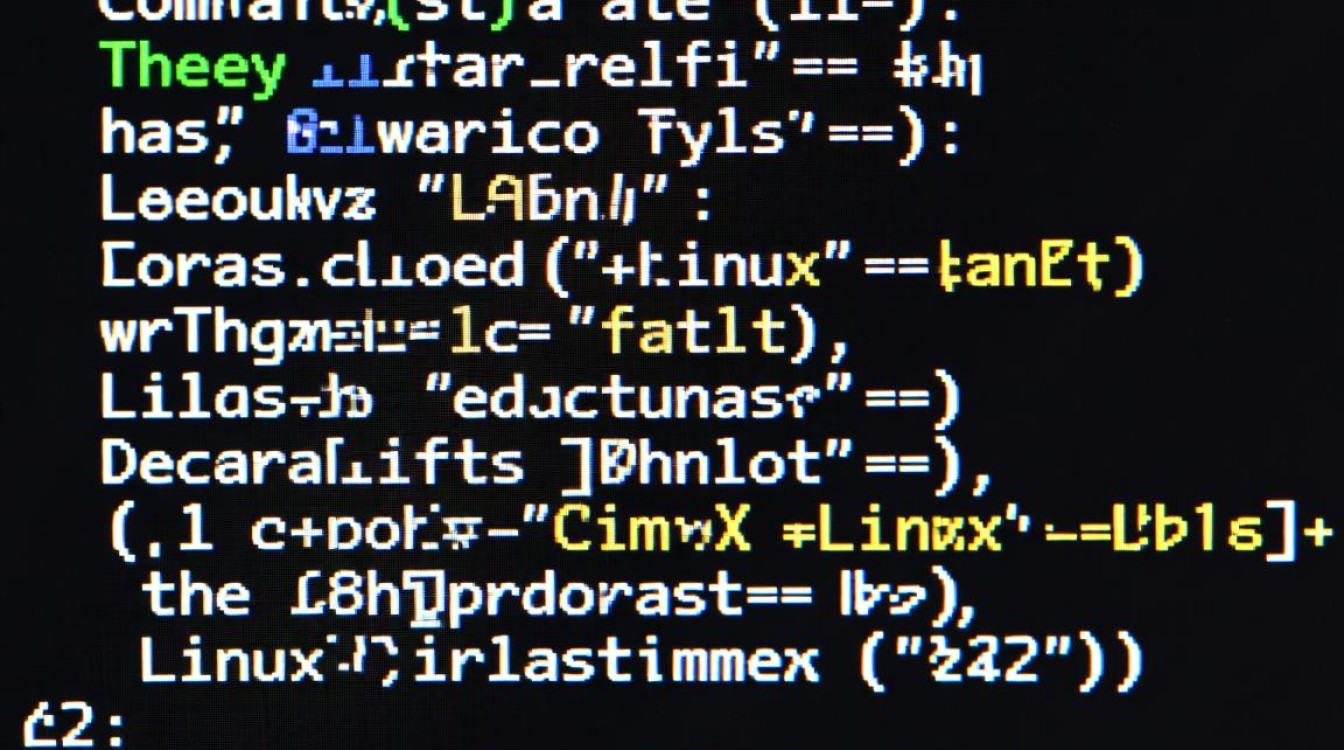
在Linux系统中,系统调用是用户空间程序与内核空间交互的桥梁,钩子函数可以用于拦截系统调用,实现对系统调用的控制,以下是一个简单的示例:
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
asmlinkage long sys_test_hook(void) {
printk(KERN_INFO "Hooked sys_test_hook\n");
return 0;
}
module_init(test_hook_init);
module_exit(test_hook_exit);
static int __init test_hook_init(void) {
sys_call_table[SYS_test_hook] = sys_test_hook;
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_hook_exit(void) {
sys_call_table[SYS_test_hook] = NULL;
}
在上面的示例中,我们定义了一个名为sys_test_hook的系统调用,并将其添加到系统调用表中,当执行sys_test_hook系统调用时,钩子函数将被调用,并输出相应的信息。
钩子函数在进程管理中的应用
在Linux系统中,进程管理是操作系统的重要组成部分,钩子函数可以用于监控、控制进程的创建、执行和销毁,以下是一个简单的示例:

#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
static struct task_struct *new_task(struct task_struct *p) {
printk(KERN_INFO "New task created\n");
return p;
}
static int __init init_task_hook(void) {
current->fn = new_task;
return 0;
}
static void __exit exit_task_hook(void) {
current->fn = NULL;
}
在上面的示例中,我们通过修改current->fn指针,将new_task函数作为钩子函数添加到进程管理中,每当创建新进程时,钩子函数都会被调用,并输出相应的信息。
钩子函数在文件系统操作中的应用
在Linux系统中,文件系统操作是用户空间程序与文件系统交互的桥梁,钩子函数可以用于拦截文件系统操作,实现对文件系统的控制,以下是一个简单的示例:
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static int hook_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk(KERN_INFO "File opened\n");
return 0;
}
static int hook_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) {
printk(KERN_INFO "File released\n");
return 0;
}
static int __init file_system_hook_init(void) {
inode_operations hook_inode_ops = {
.open = hook_open,
.release = hook_release,
};
inode_set_inode_ops(inode, &hook_inode_ops);
return 0;
}
static void __exit file_system_hook_exit(void) {
inode_set_inode_ops(inode, NULL);
}
在上面的示例中,我们定义了hook_open和hook_release两个钩子函数,用于拦截文件打开和释放操作,通过修改inode_set_inode_ops函数,我们将钩子函数添加到文件系统中。

钩子函数在Linux系统中具有广泛的应用,可以用于拦截、控制各种事件和过程,掌握钩子函数的原理和应用,对于Linux系统开发具有重要意义。