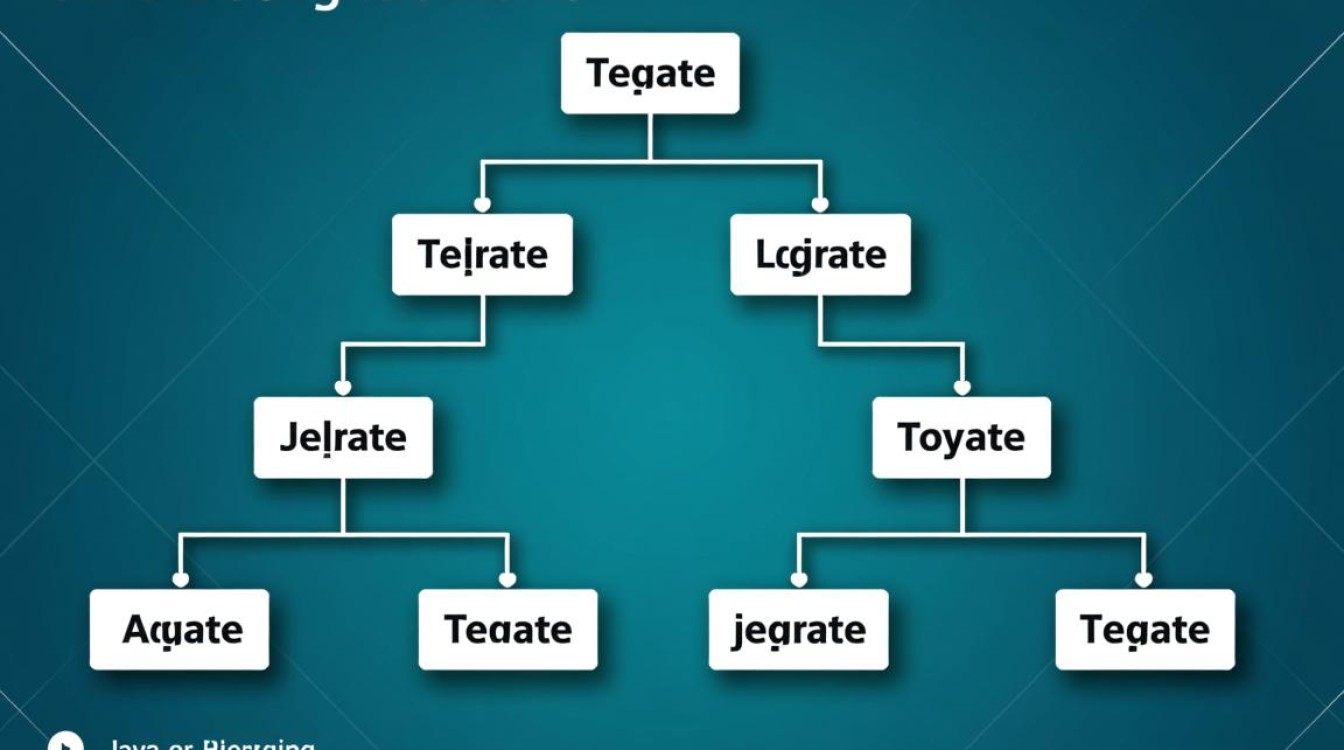
在Java中输出树形结构通常涉及到递归或者迭代的方法,树形结构是一种广泛用于数据存储和检索的数据结构,它由节点组成,每个节点可以有零个或多个子节点,以下是一些常用的方法来在Java中输出树形结构。

使用递归输出树形结构
递归是一种常用的方法来处理树形结构,因为它能够自然地映射到树的结构上,以下是一个简单的例子,展示了如何使用递归输出树形结构:
class TreeNode {
int value;
List<TreeNode> children;
public TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addChild(TreeNode child) {
children.add(child);
}
}
public class TreePrinter {
public static void printTree(TreeNode root, int level) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println(root.value);
for (TreeNode child : root.children) {
printTree(child, level + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode child1 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode child2 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode child3 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode child4 = new TreeNode(5);
root.addChild(child1);
root.addChild(child2);
child1.addChild(child3);
child1.addChild(child4);
printTree(root, 0);
}
}
使用迭代输出树形结构
虽然递归是处理树形结构的一种自然方式,但在某些情况下,你可能需要使用迭代来避免栈溢出或者更高效地处理大型树,以下是一个使用迭代输出树形结构的例子:
import java.util.Stack;
class TreeNode {
int value;
List<TreeNode> children;
public TreeNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addChild(TreeNode child) {
children.add(child);
}
}
public class TreePrinter {
public static void printTreeIterative(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode current = stack.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < current.children.size(); i++) {
stack.push(current.children.get(i));
}
System.out.println(current.value);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode child1 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode child2 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode child3 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode child4 = new TreeNode(5);
root.addChild(child1);
root.addChild(child2);
child1.addChild(child3);
child1.addChild(child4);
printTreeIterative(root);
}
}
经验案例
在处理大型树形结构时,递归方法可能会导致栈溢出错误,在这种情况下,使用迭代方法可以有效地避免这个问题,在处理社交网络中的好友关系时,你可能需要遍历一个包含数百万节点的树,使用迭代方法可以确保即使在最坏的情况下也不会耗尽调用栈。
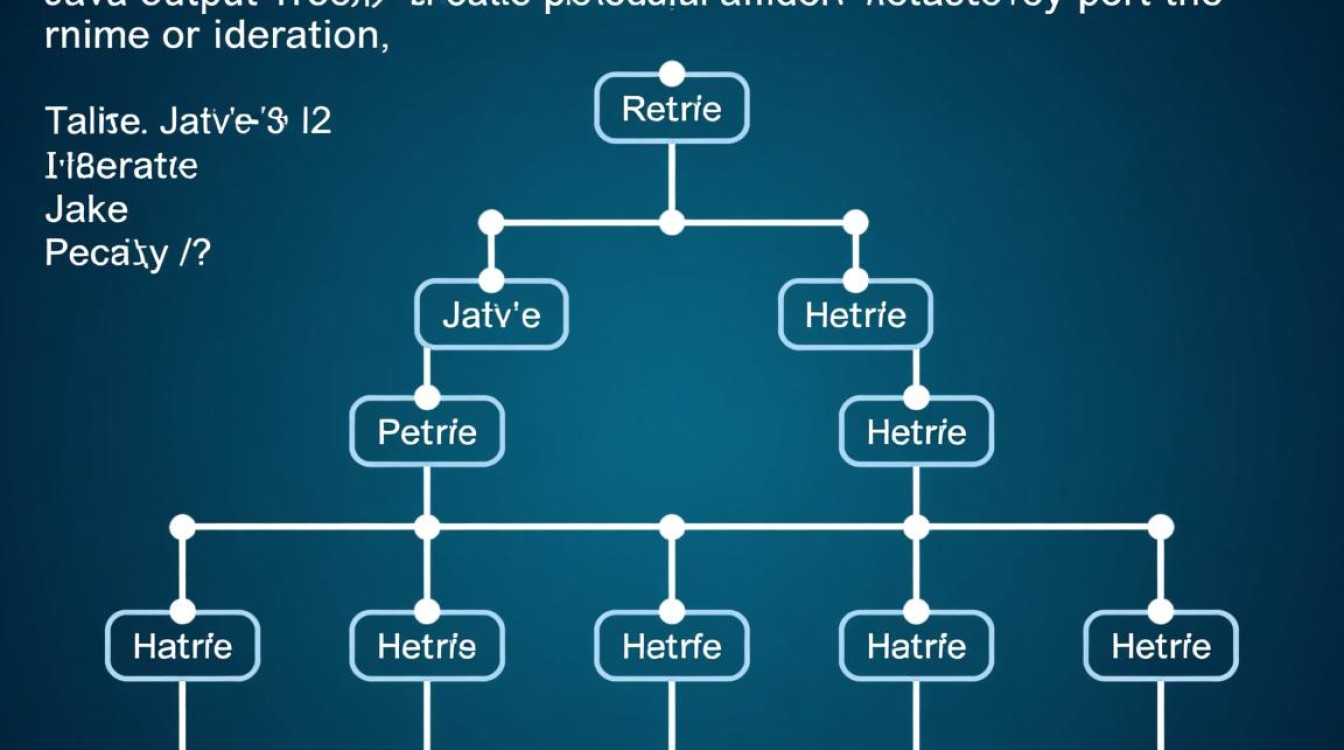
FAQs
Q1: 为什么递归方法可能会导致栈溢出错误?
A1: 当递归方法处理非常大的树时,每次递归调用都会在调用栈上添加一个新的帧,如果树的高度非常大,调用栈可能会填满,导致栈溢出错误。
Q2: 迭代方法在处理树形结构时有什么优势?
A2: 迭代方法可以避免递归方法可能导致的栈溢出错误,并且在某些情况下可能更高效,迭代方法通常更容易理解和实现。
国内文献权威来源
《Java数据结构与算法》
《Java编程思想》
《Java核心技术》
《深入理解Java虚拟机》
《Java并发编程实战》