在JavaWeb开发中,种类查询功能是常见的需求,它允许用户根据不同的条件筛选和检索数据,例如电商平台的商品分类查询、新闻系统的文章类型查询等,实现一个高效、可维护的种类查询功能,需要结合前端交互、后端逻辑设计和数据库优化等多个环节,本文将从需求分析、数据库设计、后端实现、前端交互及性能优化等方面,详细探讨如何在JavaWeb项目中编写种类查询功能。
需求分析与功能设计
在开始编码前,需明确种类查询的具体需求,种类查询涉及多个维度的筛选条件,
- 基础筛选:按种类名称、父级种类、状态(启用/禁用)等查询;
- 组合查询:支持多条件组合,如“名称包含关键词+状态为启用+父级种类为XX”;
- 分页查询:当数据量较大时,需分页返回结果,避免一次性加载过多数据;
- 排序功能:支持按创建时间、名称等字段排序。
根据需求,设计查询请求参数(如DTO)和响应结果(包含分页信息和数据列表),确保接口清晰易用。
数据库设计与表结构
种类查询的核心是数据存储,合理的数据库设计能提升查询效率,种类信息可采用父子级结构存储,
- 种类表(category):
id:主键, bigint 自增;name:种类名称, varchar(50),非空;parent_id:父级种类ID, bigint,默认0(0表示顶级种类);status:状态, tinyint(0禁用,1启用),默认1;sort_order:排序权重, int,默认0;create_time:创建时间, datetime;update_time:更新时间, datetime。
若涉及多级分类(如商品的一级、二级分类),可通过递归查询或闭包表(closure table)优化查询性能。
后端实现:分层设计与代码编写
JavaWeb后端开发通常采用MVC模式,分为控制层(Controller)、服务层(Service)、数据访问层(DAO/Repository),以下是种类查询的核心实现步骤:
数据访问层(DAO/Repository)
使用MyBatis或JPA操作数据库,定义查询方法,通过MyBatis的动态SQL实现多条件组合查询:
<!-- CategoryMapper.xml -->
<select id="selectByCondition" resultType="com.example.entity.Category">
SELECT * FROM category
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{name}, '%')
</if>
<if test="parentId != null">
AND parent_id = #{parentId}
</if>
<if test="status != null">
AND status = #{status}
</if>
</where>
ORDER BY sort_order ASC, create_time DESC
</select>
接口定义:
public interface CategoryMapper {
List<Category> selectByCondition(CategoryQueryDTO queryDTO);
}
服务层(Service)
处理业务逻辑,包括参数校验、组合查询、分页处理等,使用Spring PageHelper实现分页:
@Service
public class CategoryServiceImpl implements CategoryService {
@Autowired
private CategoryMapper categoryMapper;
@Override
public PageInfo<Category> queryByPage(CategoryQueryDTO queryDTO) {
PageHelper.startPage(queryDTO.getPageNum(), queryDTO.getPageSize());
List<Category> categories = categoryMapper.selectByCondition(queryDTO);
return new PageInfo<>(categories);
}
}
CategoryQueryDTO为查询条件对象,包含分页参数(pageNum、pageSize)和筛选条件(name、parentId、status)。
控制层(Controller)
接收前端请求,调用服务层处理并返回结果,使用RESTful风格设计接口:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/categories")
public class CategoryController {
@Autowired
private CategoryService categoryService;
@GetMapping("/query")
public Result<PageInfo<Category>> queryCategories(CategoryQueryDTO queryDTO) {
PageInfo<Category> result = categoryService.queryByPage(queryDTO);
return Result.success(result);
}
}
Result为统一响应对象,包含状态码、数据和消息,便于前端解析。
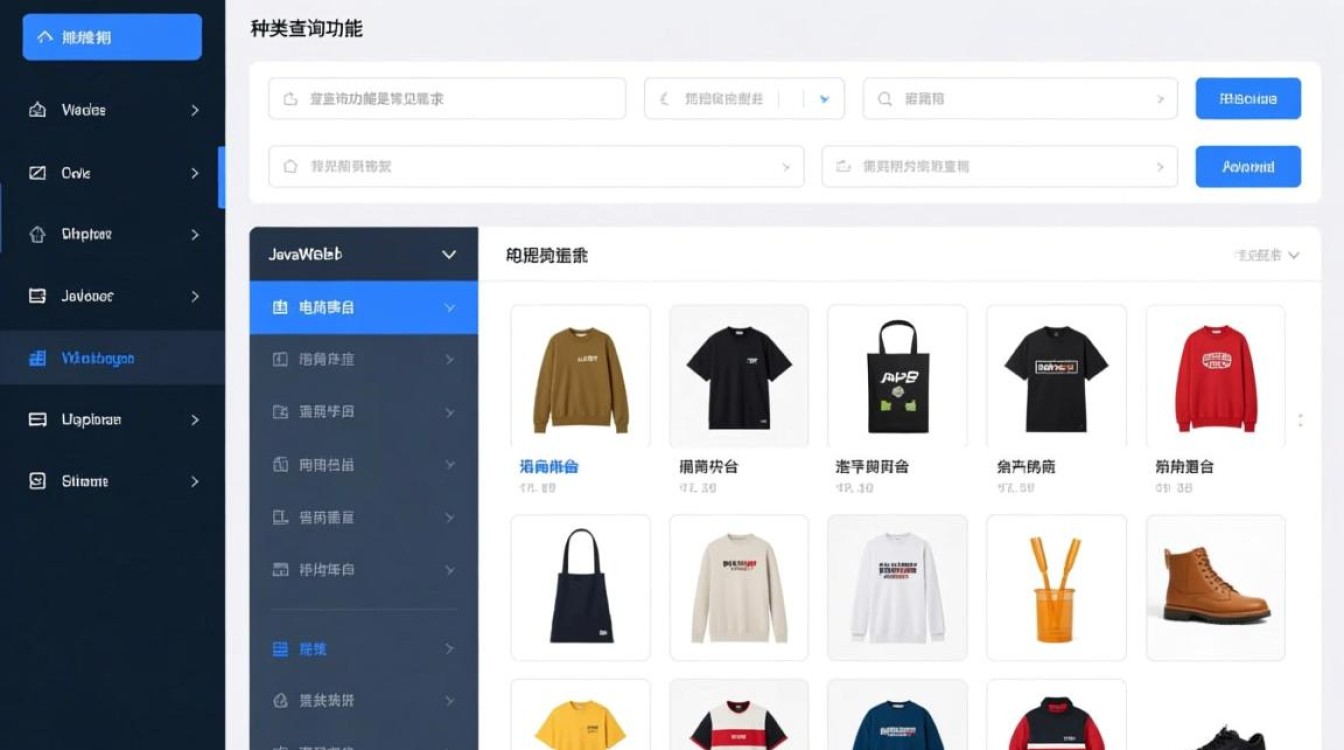
前端交互:页面设计与请求实现
前端需提供查询表单和结果展示区域,通过AJAX发送请求并动态渲染数据,以下是基于Vue.js的实现示例:
查询表单
<div class="query-form">
<el-form :inline="true" :model="queryForm" @submit.native.prevent="handleQuery">
<el-form-item label="种类名称">
<el-input v-model="queryForm.name" placeholder="请输入名称" clearable />
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="父级种类">
<el-select v-model="queryForm.parentId" placeholder="请选择父级种类" clearable>
<el-option
v-for="item in parentCategories"
:key="item.id"
:label="item.name"
:value="item.id"
/>
</el-select>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="状态">
<el-select v-model="queryForm.status" placeholder="请选择状态" clearable>
<el-option label="启用" :value="1" />
<el-option label="禁用" :value="0" />
</el-select>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="handleQuery">查询</el-button>
<el-button @click="resetQuery">重置</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
数据表格与分页
<el-table :data="categoryList" v-loading="loading">
<el-table-column prop="name" label="种类名称" />
<el-table-column prop="parentName" label="父级种类" />
<el-table-column prop="status" label="状态">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-tag :type="scope.row.status === 1 ? 'success' : 'danger'">
{{ scope.row.status === 1 ? '启用' : '禁用' }}
</el-tag>
</template>
</el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="createTime" label="创建时间" />
</el-table>
<div class="pagination">
<el-pagination
background
@size-change="handleSizeChange"
@current-change="handleCurrentChange"
:current-page="queryForm.pageNum"
:page-sizes="[10, 20, 50, 100]"
:page-size="queryForm.pageSize"
layout="total, sizes, prev, pager, next, jumper"
:total="total"
/>
</div>
JavaScript逻辑
export default {
data() {
return {
queryForm: {
pageNum: 1,
pageSize: 10,
name: '',
parentId: null,
status: null
},
categoryList: [],
total: 0,
loading: false,
parentCategories: []
};
},
created() {
this.fetchParentCategories();
this.queryCategories();
},
methods: {
async queryCategories() {
this.loading = true;
try {
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/categories/query', { params: this.queryForm });
this.categoryList = res.data.list;
this.total = res.data.total;
} finally {
this.loading = false;
}
},
handleQuery() {
this.queryForm.pageNum = 1;
this.queryCategories();
},
resetQuery() {
this.queryForm = {
pageNum: 1,
pageSize: 10,
name: '',
parentId: null,
status: null
};
this.queryCategories();
},
handleSizeChange(val) {
this.queryForm.pageSize = val;
this.queryCategories();
},
handleCurrentChange(val) {
this.queryForm.pageNum = val;
this.queryCategories();
},
async fetchParentCategories() {
const res = await this.$http.get('/api/categories/parent');
this.parentCategories = res.data;
}
}
};
性能优化与注意事项
-
数据库索引优化:
- 在
name、parent_id、status等查询字段上建立索引,避免全表扫描; - 对排序字段(如
sort_order)建立索引,提升排序效率。
- 在
-
缓存机制:
- 对于不常变动的种类数据(如父级分类列表),可使用Redis缓存,减少数据库查询压力;
- 采用
@Cacheable注解(Spring Cache)实现方法级缓存。
-
分页优化:
- 若数据量极大(如百万级),避免深度分页(如查询第100页),可采用“延迟关联”优化:先通过
id分页,再关联查询其他字段。
- 若数据量极大(如百万级),避免深度分页(如查询第100页),可采用“延迟关联”优化:先通过
-
参数校验与安全:
- 后端需对查询参数进行非空校验、长度校验,防止SQL注入(MyBatis的可自动过滤SQL注入);
- 前端对输入内容进行脱义处理,避免XSS攻击。
种类查询功能的实现需要前后端协同设计,从数据库表结构到接口定义,再到前端交互体验,每个环节都需细致处理,后端通过动态SQL和分页插件灵活处理查询条件,前端通过组件化开发提升用户体验,再结合索引优化和缓存机制,可确保功能高效稳定,在实际开发中,还需根据业务场景调整细节,例如支持多级分类的递归查询、模糊查询的匹配规则等,以满足多样化需求。


















